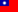
MaxOne High-Density Microelectrode Array (HD-MEA) System

MaxOne – the most powerful electrophysiological platform for recording and stimulating electrogenic cells in vitro. MaxOne is a high-density microelectrode array system in a single-well format.
Key Features


High-resolution and high-quality data while tracking dynamic changes at cellular, subcellular and network levels.

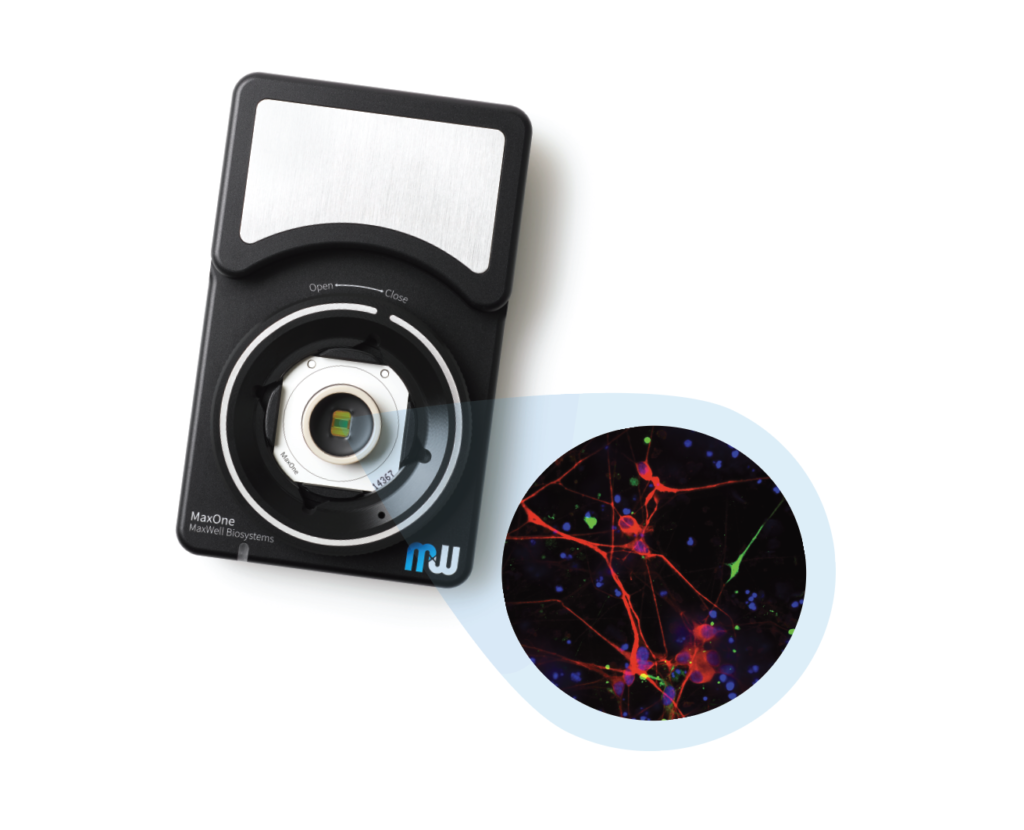
Smallest signals capture (uV) thanks to low-noise recording channels and high electrode density.

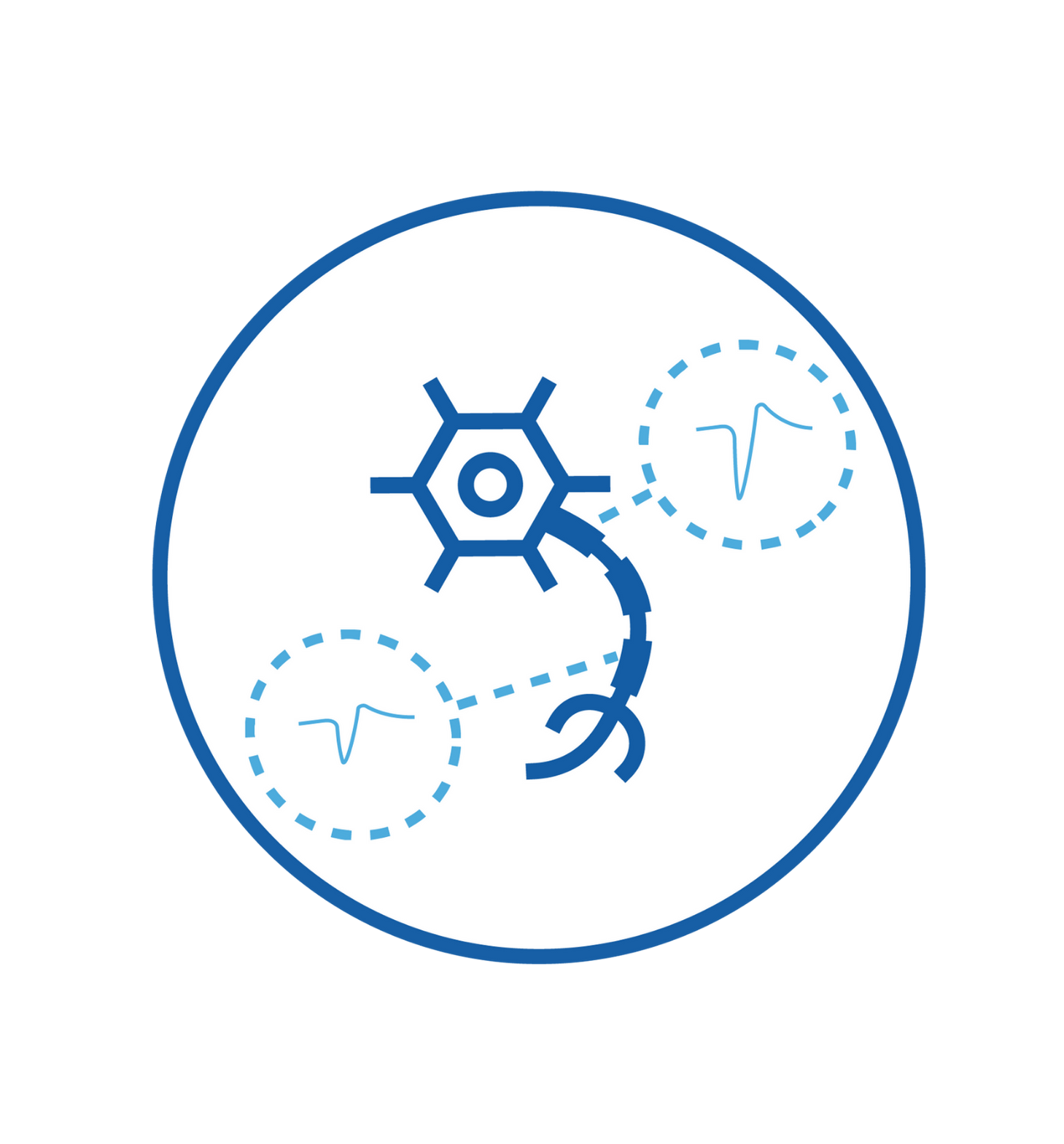
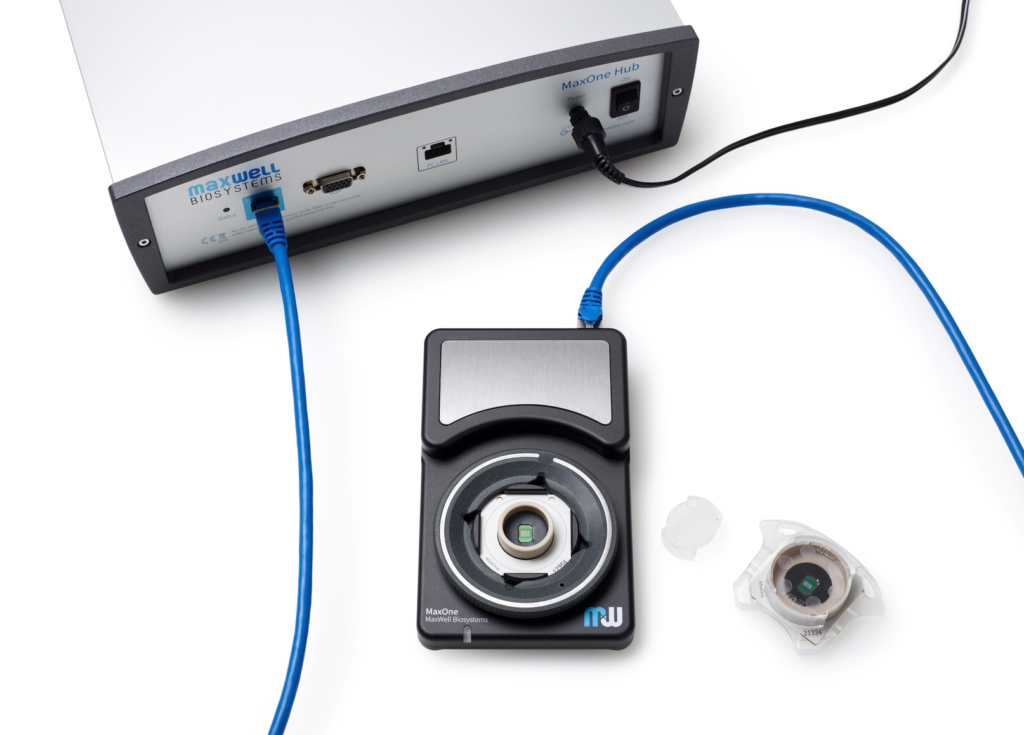
Compactly built, MaxOne Recording Unit can be flexibly installed in various environments and is compatible with other devices for both cultured samples and acute tissues.

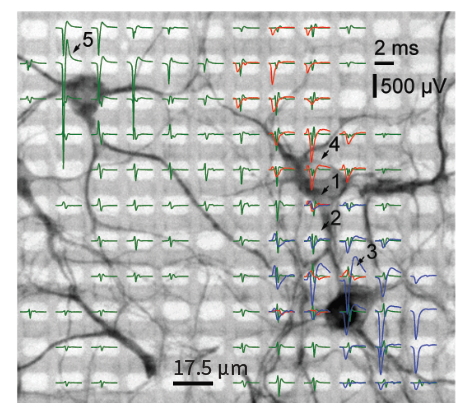
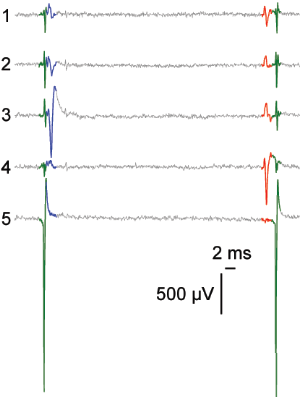
Optimized recordings strategies to analyze the entire culture at individual neuronal levels, increasing data reproducibility and statistical power.

Cell development, maturation, or compound effects assess by performing longitudinal experiments over the course of days, weeks, and months.


Non-invasive and label-free recordings, eliminating any potential side effects associated with the use of dyes and prolonged exposure to light.
Product Overview
MaxWell Biosystems’s MaxOne is a CMOS-based HD-MEA, an electrical imaging system for neuroscience, drug discovery, and cell assessment applications. MaxOne captures high-quality signals at subcellular resolution from long-term culture experiments and acute tissue experiments (e.g., brain slices, retina).

3’625 Electrodes/mm2
Low-Noise Readouts
Flexible Electrical Stimulation

Network level
Cellular level
Subcellular level
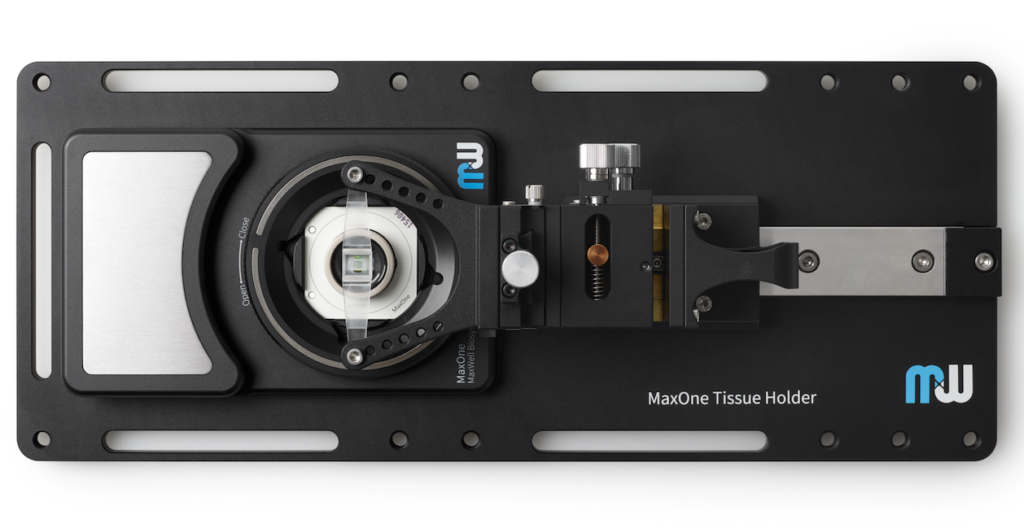

MaxOne HD-MEA system can be flexibly installed in diverse environments. For instance, MaxOne Recording Unit can operate long-term inside cell-culture incubators, and can be integrated with perfusion systems, enabling users to perform acute tissue recordings. Additionally, the system is compatible with other devices, such as being placed under an upright microscope for imaging and microscopy purposes, and integrated with tissue holders for acute tissue experiments.
Learn About MaxOne AccessoriesAll consumable MaxOne Chips share the same core features of our HD-MEA technology but differs in ways that allows them to be more suitable for cultured or acute samples.
Learn About MaxOne Chips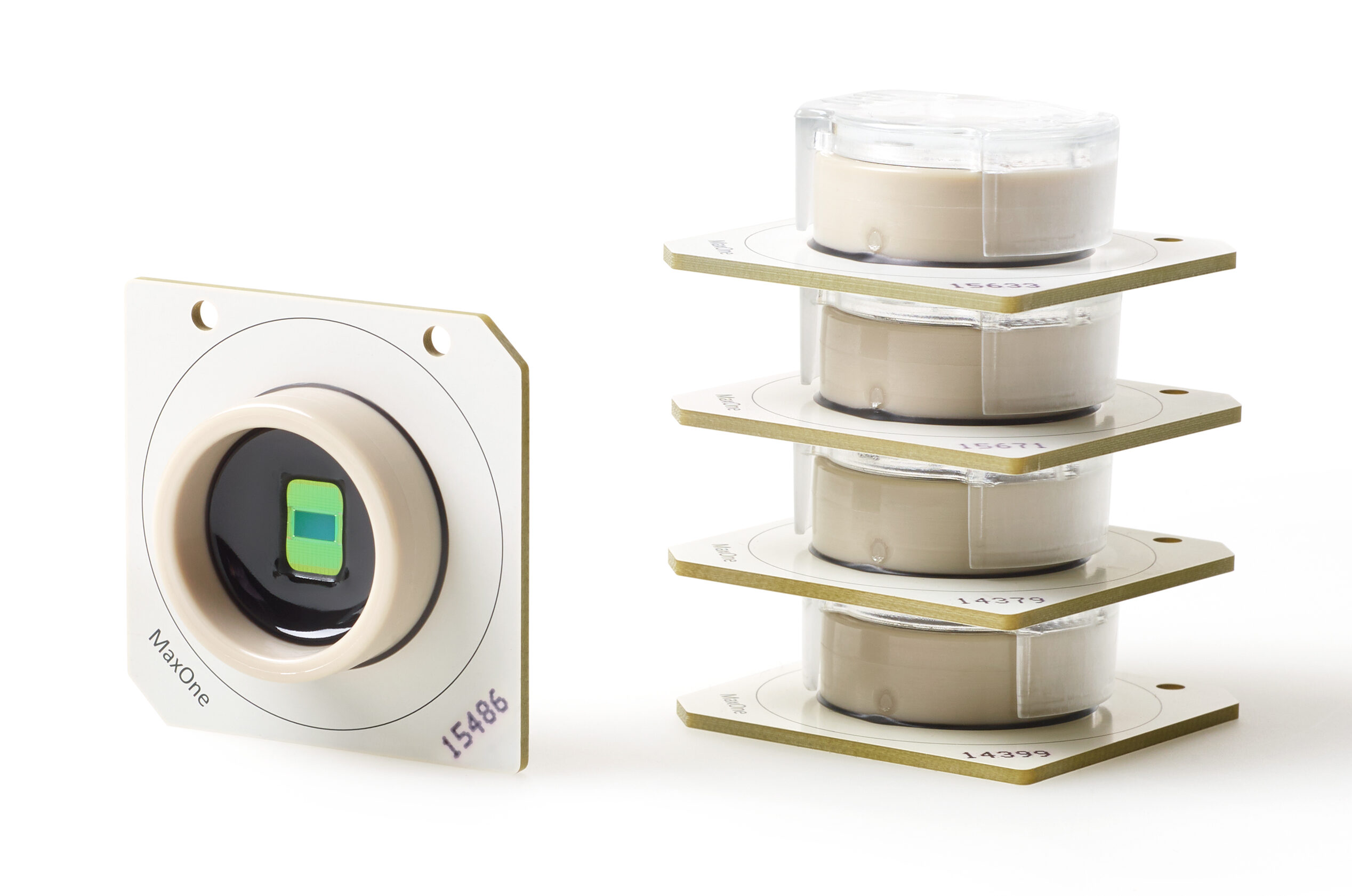

MaxOne System


| MaxOne System Features | ||
|---|---|---|
| Components | Hub Recording Unit | |
| System status indicator | LED | |
| Dimension (L x W x H) | Hub: 18.5 x 28x 9 cm3 Recording Unit: 15 x 9.5 x 2.5 cm3 | |
| Chip compatibility | Small (PSM) Large (PLM) | |
| Incubator friendly | Yes, for the Recording Unit |
This might also interest you
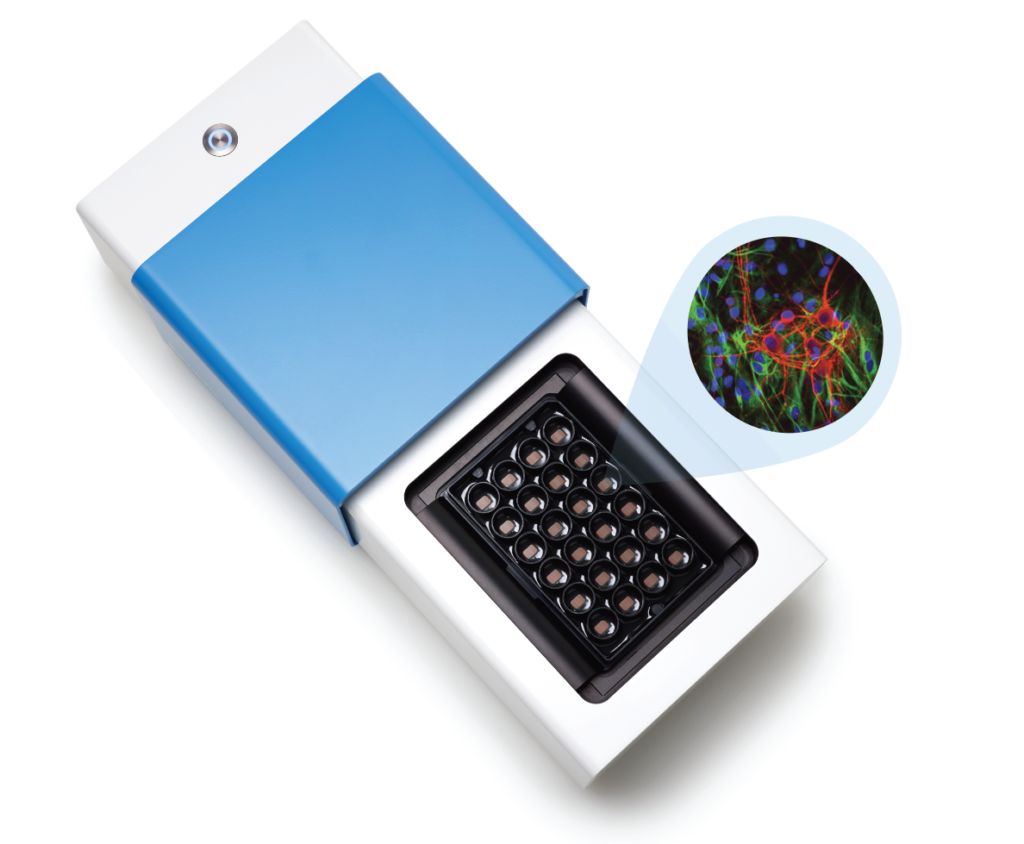


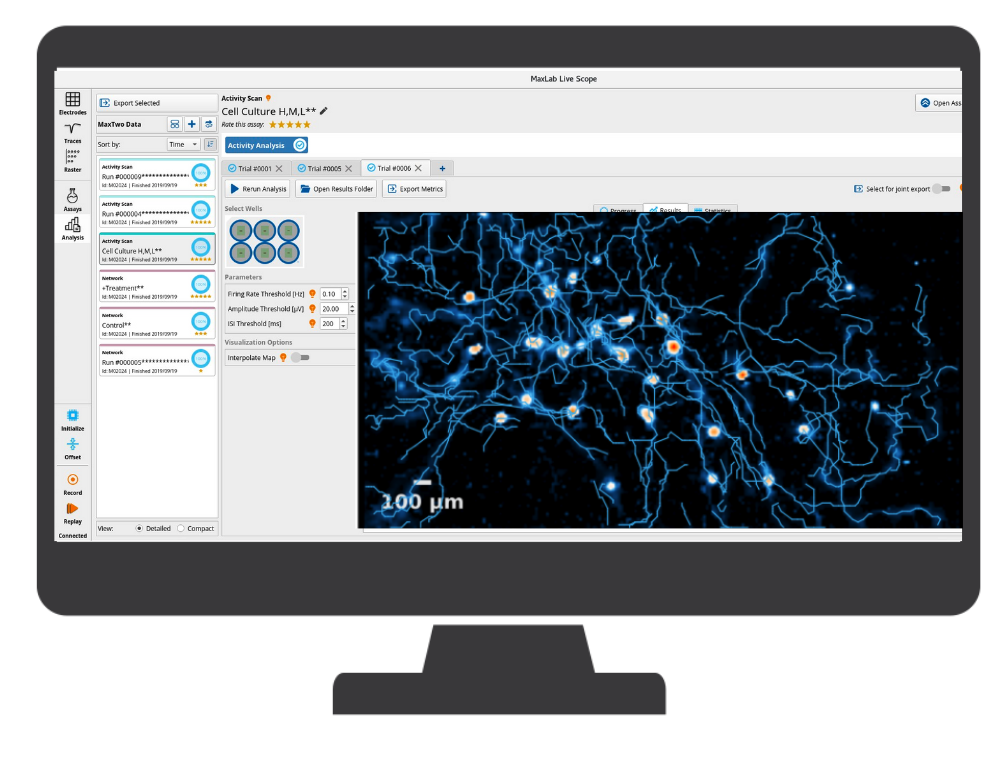

Publications Featuring the MaxOne
  | McSweeney, Danny; Gabriel, Rafael; Jin, Kang; Pang, Zhiping P; Aronow, Bruce; Pak, ChangHui Loss of Neurodevelopmental Gene CASK Disrupts Neural Connectivity in Human Cortical Excitatory Neurons Journal Article BioRxiv, 2022. @article{McSweeney2022, title = {Loss of Neurodevelopmental Gene CASK Disrupts Neural Connectivity in Human Cortical Excitatory Neurons}, author = {Danny McSweeney and Rafael Gabriel and Kang Jin and Zhiping P. Pang and Bruce Aronow and ChangHui Pak}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.14.480404}, doi = {10.1101/2022.02.14.480404}, year = {2022}, date = {2022-02-15}, journal = {BioRxiv}, abstract = {Loss-of-function (LOF) mutations in CASK cause severe developmental phenotypes, including microcephaly with pontine and cerebellar hypoplasia, X-linked intellectual disability, and autism. Unraveling the pathogenesis of CASK-related disorders has been challenging due to limited human cellular models to study the dynamic roles of this molecule during neuronal and synapse development. Here, we generated CASK knockout (KO) isogenic cell lines from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) using CRISPR/Cas9 and examined gene expression, morphometrics and synaptic function of induced neuronal cells during development. While young (immature) CASK KO neurons show robust neuronal outgrowth, mature CASK KO neurons displayed severe defects in synaptic transmission and synchronized burst activity without compromising neuronal morphology and synapse numbers. In developing human cortical neurons, CASK functions to promote both structural integrity and establishment of cortical excitatory neuronal networks. These results lay the foundation for future studies identifying suppressors of such phenotypes relevant to human patients.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Loss-of-function (LOF) mutations in CASK cause severe developmental phenotypes, including microcephaly with pontine and cerebellar hypoplasia, X-linked intellectual disability, and autism. Unraveling the pathogenesis of CASK-related disorders has been challenging due to limited human cellular models to study the dynamic roles of this molecule during neuronal and synapse development. Here, we generated CASK knockout (KO) isogenic cell lines from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) using CRISPR/Cas9 and examined gene expression, morphometrics and synaptic function of induced neuronal cells during development. While young (immature) CASK KO neurons show robust neuronal outgrowth, mature CASK KO neurons displayed severe defects in synaptic transmission and synchronized burst activity without compromising neuronal morphology and synapse numbers. In developing human cortical neurons, CASK functions to promote both structural integrity and establishment of cortical excitatory neuronal networks. These results lay the foundation for future studies identifying suppressors of such phenotypes relevant to human patients. |
  | Paulsen, Bruna; Velasco, Silvia; Kedaigle, Amanda J; Pigoni, Martina; Quadrato, Giorgia; Deo, Anthony J; Adiconis, Xian; Uzquiano, Ana; Sartore, Rafaela; Yang, Sung Min; Simmons, Sean K; Symvoulidis, Panagiotis; Kim, Kwanho; Tsafou, Kalliopi; Podury, Archana; Abbate, Catherine; Tucewicz, Ashley; Smith, Samantha N; Albanese, Alexandre; Barrett, Lindy; Sanjana, Neville E; Shi, Xi; Chung, Kwanghun; Lage, Kasper; Boyden, Edward S; andJoshua Levin, Aviv Regev Z; Arlotta, Paola Autism genes converge on asynchronous development of shared neuron classes Journal Article Nature, 602 , pp. 268–273, 2022. @article{Paulsen2022, title = {Autism genes converge on asynchronous development of shared neuron classes}, author = {Bruna Paulsen and Silvia Velasco and Amanda J. Kedaigle and Martina Pigoni and Giorgia Quadrato and Anthony J. Deo and Xian Adiconis and Ana Uzquiano and Rafaela Sartore and Sung Min Yang and Sean K. Simmons and Panagiotis Symvoulidis and Kwanho Kim and Kalliopi Tsafou and Archana Podury and Catherine Abbate and Ashley Tucewicz and Samantha N. Smith and Alexandre Albanese and Lindy Barrett and Neville E. Sanjana and Xi Shi and Kwanghun Chung and Kasper Lage and Edward S. Boyden and Aviv Regev andJoshua Z. Levin and Paola Arlotta }, url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04358-6}, doi = {10.1038/s41586-021-04358-6}, year = {2022}, date = {2022-02-02}, journal = {Nature}, volume = {602}, pages = {268–273}, abstract = {Genetic risk for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is associated with hundreds of genes spanning a wide range of biological functions1,2,3,4,5,6. The alterations in the human brain resulting from mutations in these genes remain unclear. Furthermore, their phenotypic manifestation varies across individuals7,8. Here we used organoid models of the human cerebral cortex to identify cell-type-specific developmental abnormalities that result from haploinsufficiency in three ASD risk genes—SUV420H1 (also known as KMT5B), ARID1B and CHD8—in multiple cell lines from different donors, using single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis of more than 745,000 cells and proteomic analysis of individual organoids, to identify phenotypic convergence. Each of the three mutations confers asynchronous development of two main cortical neuronal lineages—γ-aminobutyric-acid-releasing (GABAergic) neurons and deep-layer excitatory projection neurons—but acts through largely distinct molecular pathways. Although these phenotypes are consistent across cell lines, their expressivity is influenced by the individual genomic context, in a manner that is dependent on both the risk gene and the developmental defect. Calcium imaging in intact organoids shows that these early-stage developmental changes are followed by abnormal circuit activity. This research uncovers cell-type-specific neurodevelopmental abnormalities that are shared across ASD risk genes and are finely modulated by human genomic context, finding convergence in the neurobiological basis of how different risk genes contribute to ASD pathology.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Genetic risk for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is associated with hundreds of genes spanning a wide range of biological functions1,2,3,4,5,6. The alterations in the human brain resulting from mutations in these genes remain unclear. Furthermore, their phenotypic manifestation varies across individuals7,8. Here we used organoid models of the human cerebral cortex to identify cell-type-specific developmental abnormalities that result from haploinsufficiency in three ASD risk genes—SUV420H1 (also known as KMT5B), ARID1B and CHD8—in multiple cell lines from different donors, using single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis of more than 745,000 cells and proteomic analysis of individual organoids, to identify phenotypic convergence. Each of the three mutations confers asynchronous development of two main cortical neuronal lineages—γ-aminobutyric-acid-releasing (GABAergic) neurons and deep-layer excitatory projection neurons—but acts through largely distinct molecular pathways. Although these phenotypes are consistent across cell lines, their expressivity is influenced by the individual genomic context, in a manner that is dependent on both the risk gene and the developmental defect. Calcium imaging in intact organoids shows that these early-stage developmental changes are followed by abnormal circuit activity. This research uncovers cell-type-specific neurodevelopmental abnormalities that are shared across ASD risk genes and are finely modulated by human genomic context, finding convergence in the neurobiological basis of how different risk genes contribute to ASD pathology. |
  | Kagan, Brett J; Kitchen, Andy C; Tran, Nhi T; Parker, Bradyn J; Bhat, Anjali; Rollo, Ben; Razi, Adeel; Friston, Karl J In vitro neurons learn and exhibit sentience when embodied in a simulated game-world Journal Article BioRxiv, 2021. @article{Kagan2021, title = {In vitro neurons learn and exhibit sentience when embodied in a simulated game-world}, author = {Brett J. Kagan and Andy C. Kitchen and Nhi T. Tran and Bradyn J. Parker and Anjali Bhat and Ben Rollo and Adeel Razi and Karl J. Friston}, url = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.02.471005v1 }, doi = {10.1101/2021.12.02.471005}, year = {2021}, date = {2021-12-03}, journal = {BioRxiv}, abstract = {Human brain organoids replicate much of the cellular diversity and developmental anatomy of the human brain. However, the physiological behavior of neuronal circuits within organoids remains relatively under-explored. With high-density CMOS microelectrode arrays (26,400 electrodes) and shank electrodes (960 electrodes), we probed broadband and three-dimensional extracellular field recordings generated by spontaneous activity of human brain organoids. These recordings simultaneously captured local field potentials (LFPs) and single-unit activity extracted through spike sorting. From spiking activity, we estimated a directed functional connectivity graph of synchronous neural network activity, which showed a large number of weak functional connections enmeshed within a network skeleton of significantly fewer strong connections. Treatment of the organoid with a benzodiazepine induced a reproducible signature response that shortened the inter-burst intervals, increased the uniformity of the firing pattern within each burst and decreased the population of weakly connected edges. Simultaneously examining the spontaneous LFPs and their phase alignment to spiking showed that spike bursts were coherent with theta oscillations in the LFPs. Our results demonstrate that human brain organoids have self-organized neuronal assemblies of sufficient size, cellular orientation, and functional connectivity to co-activate and generate field potentials from their collective transmembrane currents that phase-lock to spiking activity. These results point to the potential of brain organoids for the study of neuropsychiatric diseases, drug mechanisms, and the effects of external stimuli upon neuronal networks.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Human brain organoids replicate much of the cellular diversity and developmental anatomy of the human brain. However, the physiological behavior of neuronal circuits within organoids remains relatively under-explored. With high-density CMOS microelectrode arrays (26,400 electrodes) and shank electrodes (960 electrodes), we probed broadband and three-dimensional extracellular field recordings generated by spontaneous activity of human brain organoids. These recordings simultaneously captured local field potentials (LFPs) and single-unit activity extracted through spike sorting. From spiking activity, we estimated a directed functional connectivity graph of synchronous neural network activity, which showed a large number of weak functional connections enmeshed within a network skeleton of significantly fewer strong connections. Treatment of the organoid with a benzodiazepine induced a reproducible signature response that shortened the inter-burst intervals, increased the uniformity of the firing pattern within each burst and decreased the population of weakly connected edges. Simultaneously examining the spontaneous LFPs and their phase alignment to spiking showed that spike bursts were coherent with theta oscillations in the LFPs. Our results demonstrate that human brain organoids have self-organized neuronal assemblies of sufficient size, cellular orientation, and functional connectivity to co-activate and generate field potentials from their collective transmembrane currents that phase-lock to spiking activity. These results point to the potential of brain organoids for the study of neuropsychiatric diseases, drug mechanisms, and the effects of external stimuli upon neuronal networks. |
  | Kubota, Tomoyuki; Takahashi, Hirokazu; and Nakajima, Kohei Unifying framework for information processing in stochastically driven dynamical systems Journal Article Physical Review Research, 2021. @article{Kubota2023, title = {Unifying framework for information processing in stochastically driven dynamical systems}, author = {Tomoyuki Kubota and Hirokazu Takahashi and and Kohei Nakajima}, url = {https://journals.aps.org/prresearch/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.043135}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.043135}, year = {2021}, date = {2021-11-23}, journal = {Physical Review Research}, abstract = {A dynamical system is an information processing apparatus that encodes input streams from the external environment to its state and processes them through state transitions. The information processing capacity (IPC) is an excellent tool that comprehensively evaluates these processed inputs, providing details of unknown information processing in black box systems; however, this measure can be applied only to time-invariant systems. This paper extends the applicable range to time-variant systems and further reveals that the IPC is equivalent to coefficients of polynomial chaos (PC) expansion in more general dynamical systems. To achieve this objective, we tackle three issues. First, we establish a connection between the IPC for time-invariant systems and PC expansion, which is a type of polynomial expansion using orthogonal functions of input history as bases. We prove that the IPC corresponds to the squared norm of the coefficient vector of the basis in the PC expansion. Second, we show that an input following an arbitrary distribution can be used for the IPC, removing previous restrictions to specific input distributions. Third, we extend the conventional orthogonal bases to functions of both time and input history and propose the IPC for time-variant systems. To show the significance of our approach, we demonstrate that our measure can reveal information representations in not only machine learning networks but also a real, cultured neural network. Our generalized measure paves the way for unveiling the information processing capabilities of a wide variety of physical dynamics which have been left behind in nature.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } A dynamical system is an information processing apparatus that encodes input streams from the external environment to its state and processes them through state transitions. The information processing capacity (IPC) is an excellent tool that comprehensively evaluates these processed inputs, providing details of unknown information processing in black box systems; however, this measure can be applied only to time-invariant systems. This paper extends the applicable range to time-variant systems and further reveals that the IPC is equivalent to coefficients of polynomial chaos (PC) expansion in more general dynamical systems. To achieve this objective, we tackle three issues. First, we establish a connection between the IPC for time-invariant systems and PC expansion, which is a type of polynomial expansion using orthogonal functions of input history as bases. We prove that the IPC corresponds to the squared norm of the coefficient vector of the basis in the PC expansion. Second, we show that an input following an arbitrary distribution can be used for the IPC, removing previous restrictions to specific input distributions. Third, we extend the conventional orthogonal bases to functions of both time and input history and propose the IPC for time-variant systems. To show the significance of our approach, we demonstrate that our measure can reveal information representations in not only machine learning networks but also a real, cultured neural network. Our generalized measure paves the way for unveiling the information processing capabilities of a wide variety of physical dynamics which have been left behind in nature. |
  | Schenke, Maren; Prause, Hélène-Christine; Bergforth, Wiebke; Przykopanski, Adina Human-Relevant Sensitivity of iPSC-Derived Human Motor Neurons to BoNT/A1 and B1 Journal Article toxins, 2021. @article{Schenke2021, title = {Human-Relevant Sensitivity of iPSC-Derived Human Motor Neurons to BoNT/A1 and B1}, author = {Maren Schenke and Hélène-Christine Prause and Wiebke Bergforth and Adina Przykopanski}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6651/13/8/585}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080585}, year = {2021}, date = {2021-08-22}, journal = {toxins}, abstract = {The application of botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) for medical treatments necessitates a potency quantification of these lethal bacterial toxins, resulting in the use of a large number of test animals. Available alternative methods are limited in their relevance, as they are based on rodent cells or neuroblastoma cell lines or applicable for single toxin serotypes only. Here, human motor neurons (MNs), which are the physiological target of BoNTs, were generated from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and compared to the neuroblastoma cell line SiMa, which is often used in cell-based assays for BoNT potency determination. In comparison with the mouse bioassay, human MNs exhibit a superior sensitivity to the BoNT serotypes A1 and B1 at levels that are reflective of human sensitivity. SiMa cells were able to detect BoNT/A1, but with much lower sensitivity than human MNs and appear unsuitable to detect any BoNT/B1 activity. The MNs used for these experiments were generated according to three differentiation protocols, which resulted in distinct sensitivity levels. Molecular parameters such as receptor protein concentration and electrical activity of the MNs were analyzed, but are not predictive for BoNT sensitivity. These results show that human MNs from several sources should be considered in BoNT testing and that human MNs are a physiologically relevant model, which could be used to optimize current BoNT potency testing.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The application of botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) for medical treatments necessitates a potency quantification of these lethal bacterial toxins, resulting in the use of a large number of test animals. Available alternative methods are limited in their relevance, as they are based on rodent cells or neuroblastoma cell lines or applicable for single toxin serotypes only. Here, human motor neurons (MNs), which are the physiological target of BoNTs, were generated from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and compared to the neuroblastoma cell line SiMa, which is often used in cell-based assays for BoNT potency determination. In comparison with the mouse bioassay, human MNs exhibit a superior sensitivity to the BoNT serotypes A1 and B1 at levels that are reflective of human sensitivity. SiMa cells were able to detect BoNT/A1, but with much lower sensitivity than human MNs and appear unsuitable to detect any BoNT/B1 activity. The MNs used for these experiments were generated according to three differentiation protocols, which resulted in distinct sensitivity levels. Molecular parameters such as receptor protein concentration and electrical activity of the MNs were analyzed, but are not predictive for BoNT sensitivity. These results show that human MNs from several sources should be considered in BoNT testing and that human MNs are a physiologically relevant model, which could be used to optimize current BoNT potency testing. |
  | Sundberg, Maria; Pinson, Hannah; Smith, Richard S; Winden, Kellen D; Venugopal, Pooja; Tai, Derek J C; Gusella, James F; Talkowski, Michael E; Walsh, Christopher A; Tegmark, Max; Sahin, Mustafa Nature Communications, 12 (2897 ), 2021. @article{Sundberg2021, title = {16p11.2 deletion is associated with hyperactivation of human iPSC-derived dopaminergic neuron networks and is rescued by RHOA inhibition in vitro}, author = {Maria Sundberg and Hannah Pinson and Richard S. Smith and Kellen D. Winden and Pooja Venugopal and Derek J. C. Tai and James F. Gusella and Michael E. Talkowski and Christopher A. Walsh and Max Tegmark and Mustafa Sahin }, url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-23113-z}, doi = {10.1038/s41467-021-23113-z}, year = {2021}, date = {2021-05-18}, journal = {Nature Communications}, volume = {12}, number = {2897 }, abstract = {Reciprocal copy number variations (CNVs) of 16p11.2 are associated with a wide spectrum of neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders. Here, we use human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)-derived dopaminergic (DA) neurons carrying CNVs of 16p11.2 duplication (16pdup) and 16p11.2 deletion (16pdel), engineered using CRISPR-Cas9. We show that 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neurons have increased soma size and synaptic marker expression compared to isogenic control lines, while 16pdup iPSC-derived DA neurons show deficits in neuronal differentiation and reduced synaptic marker expression. The 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neurons have impaired neurophysiological properties. The 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neuronal networks are hyperactive and have increased bursting in culture compared to controls. We also show that the expression of RHOA is increased in the 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neurons and that treatment with a specific RHOA-inhibitor, Rhosin, rescues the network activity of the 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neurons. Our data suggest that 16p11.2 deletion-associated iPSC-derived DA neuron hyperactivation can be rescued by RHOA inhibition.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Reciprocal copy number variations (CNVs) of 16p11.2 are associated with a wide spectrum of neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders. Here, we use human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)-derived dopaminergic (DA) neurons carrying CNVs of 16p11.2 duplication (16pdup) and 16p11.2 deletion (16pdel), engineered using CRISPR-Cas9. We show that 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neurons have increased soma size and synaptic marker expression compared to isogenic control lines, while 16pdup iPSC-derived DA neurons show deficits in neuronal differentiation and reduced synaptic marker expression. The 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neurons have impaired neurophysiological properties. The 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neuronal networks are hyperactive and have increased bursting in culture compared to controls. We also show that the expression of RHOA is increased in the 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neurons and that treatment with a specific RHOA-inhibitor, Rhosin, rescues the network activity of the 16pdel iPSC-derived DA neurons. Our data suggest that 16p11.2 deletion-associated iPSC-derived DA neuron hyperactivation can be rescued by RHOA inhibition. |
  | Kajiwara Motoki; Nomura, Ritsuki; Goetze Felix; Kawabata Masanori; Isomura Yoshikazu; Akutsu Tatsuya; Shimono Masanori; Inhibitory neurons exhibit high controlling ability in the cortical microconnectome Journal Article PLOS Computational Biology, 2021. @article{Kajiwara2021, title = {Inhibitory neurons exhibit high controlling ability in the cortical microconnectome}, author = {Kajiwara, Motoki; Nomura, Ritsuki; Goetze, Felix; Kawabata, Masanori; Isomura, Yoshikazu; Akutsu, Tatsuya; Shimono, Masanori; }, url = {https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008846}, year = {2021}, date = {2021-04-08}, journal = {PLOS Computational Biology}, abstract = {The brain is a network system in which excitatory and inhibitory neurons keep activity bal- anced in the highly non-random connectivity pattern of the microconnectome. It is well known that the relative percentage of inhibitory neurons is much smaller than excitatory neu- rons in the cortex. So, in general, how inhibitory neurons can keep the balance with the sur- rounding excitatory neurons is an important question. There is much accumulated knowledge about this fundamental question. This study quantitatively evaluated the rela- tively higher functional contribution of inhibitory neurons in terms of not only properties of individual neurons, such as firing rate, but also in terms of topological mechanisms and con- trolling ability on other excitatory neurons. We combined simultaneous electrical recording (~2.5 hours) of ~1000 neurons in vitro, and quantitative evaluation of neuronal interactions including excitatory-inhibitory categorization. This study accurately defined recording brain anatomical targets, such as brain regions and cortical layers, by inter-referring MRI and immunostaining recordings. The interaction networks enabled us to quantify topological influence of individual neurons, in terms of controlling ability to other neurons. Especially, the result indicated that highly influential inhibitory neurons show higher controlling ability of other neurons than excitatory neurons, and are relatively often distributed in deeper layers of the cortex. Furthermore, the neurons having high controlling ability are more effectively limited in number than central nodes of k-cores, and these neurons also participate in more clustered motifs. In summary, this study suggested that the high controlling ability of inhibi- tory neurons is a key mechanism to keep balance with a large number of other excitatory neurons beyond simple higher firing rate. Application of the selection method of limited important neurons would be also applicable for the ability to effectively and selectively stimu- late E/I imbalanced disease states.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The brain is a network system in which excitatory and inhibitory neurons keep activity bal- anced in the highly non-random connectivity pattern of the microconnectome. It is well known that the relative percentage of inhibitory neurons is much smaller than excitatory neu- rons in the cortex. So, in general, how inhibitory neurons can keep the balance with the sur- rounding excitatory neurons is an important question. There is much accumulated knowledge about this fundamental question. This study quantitatively evaluated the rela- tively higher functional contribution of inhibitory neurons in terms of not only properties of individual neurons, such as firing rate, but also in terms of topological mechanisms and con- trolling ability on other excitatory neurons. We combined simultaneous electrical recording (~2.5 hours) of ~1000 neurons in vitro, and quantitative evaluation of neuronal interactions including excitatory-inhibitory categorization. This study accurately defined recording brain anatomical targets, such as brain regions and cortical layers, by inter-referring MRI and immunostaining recordings. The interaction networks enabled us to quantify topological influence of individual neurons, in terms of controlling ability to other neurons. Especially, the result indicated that highly influential inhibitory neurons show higher controlling ability of other neurons than excitatory neurons, and are relatively often distributed in deeper layers of the cortex. Furthermore, the neurons having high controlling ability are more effectively limited in number than central nodes of k-cores, and these neurons also participate in more clustered motifs. In summary, this study suggested that the high controlling ability of inhibi- tory neurons is a key mechanism to keep balance with a large number of other excitatory neurons beyond simple higher firing rate. Application of the selection method of limited important neurons would be also applicable for the ability to effectively and selectively stimu- late E/I imbalanced disease states. |
  | Idrees, Saad; Münch, Thomas A Different contrast encoding in ON and OFF visual pathways Journal Article BioRxiv, 2020. @article{Idrees2020b, title = {Different contrast encoding in ON and OFF visual pathways}, author = {Saad Idrees and Thomas A. Münch }, url = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.11.25.398230v1}, doi = {10.1101/2020.11.25.398230}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-11-26}, journal = {BioRxiv}, abstract = {Subjective visual experience builds on sensory encoding of light reflected by different objects in our environment. Most retinal ganglion cells encode changes in light intensity, quantified as contrast, rather than the absolute intensity. Mathematically, contrast is often defined as a relative change in light intensity. Activity in the visual system and perceptual responses are usually explained with such definitions of contrast. Here, for the first time, we explicitly explored how contrast is actually represented in the visual system. Using mouse retina electrophysiology, we show that response strength of OFF retinal ganglion cells does not represent relative, but absolute changes in light intensity. ON RGC response strength is governed by a combination of absolute and relative change in light intensity. This is true for a wide range of ambient light levels, at least from scotopic to high mesopic regimes. Consequently, light decrements and increments are represented asymmetrically in the retina, which may explain the asymmetries in responses to negative and positive contrast observed throughout the visual system. These findings may help to more thoroughly design and interpret vision science studies where responses are driven by contrast of the visual stimuli.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Subjective visual experience builds on sensory encoding of light reflected by different objects in our environment. Most retinal ganglion cells encode changes in light intensity, quantified as contrast, rather than the absolute intensity. Mathematically, contrast is often defined as a relative change in light intensity. Activity in the visual system and perceptual responses are usually explained with such definitions of contrast. Here, for the first time, we explicitly explored how contrast is actually represented in the visual system. Using mouse retina electrophysiology, we show that response strength of OFF retinal ganglion cells does not represent relative, but absolute changes in light intensity. ON RGC response strength is governed by a combination of absolute and relative change in light intensity. This is true for a wide range of ambient light levels, at least from scotopic to high mesopic regimes. Consequently, light decrements and increments are represented asymmetrically in the retina, which may explain the asymmetries in responses to negative and positive contrast observed throughout the visual system. These findings may help to more thoroughly design and interpret vision science studies where responses are driven by contrast of the visual stimuli. |
  | Ricci, Chiara; Frey, Urs; Obien, Marie Engelene J IEEE, 2020. @article{Ricci2020, title = {MAPSYNE: Miniaturized micropipette system combined with high-density microelectrode arrays for automated manipulation of neuronal networks in-vitro}, author = {Chiara Ricci and Urs Frey and Marie Engelene J. Obien}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9175797/}, doi = {10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9175797}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-10-08}, journal = {IEEE}, abstract = {We present MAPSYNE, a miniaturized and automated system combining a high-density microelectrode array (HD-MEA) and a movable micropipette for studying, monitoring, and perturbing neurons in vitro. The system involves an all-electrical approach to automatically move a glass micropipette towards a target location on the HD-MEA surface, without the need for a microscope. Two methods of performing blind navigation are employed, (i) stop-measure-go approach wherein the pipette moves for a predefined distance before measuring its location then the process is repeated until the pipette reaches its destination, and (ii) predictive approach wherein the pipette is continuously tracked and moved. This automated system can be applied for unsupervised single-cell manipulation of neurons in a network, such as electroporation and local delivery of compounds.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } We present MAPSYNE, a miniaturized and automated system combining a high-density microelectrode array (HD-MEA) and a movable micropipette for studying, monitoring, and perturbing neurons in vitro. The system involves an all-electrical approach to automatically move a glass micropipette towards a target location on the HD-MEA surface, without the need for a microscope. Two methods of performing blind navigation are employed, (i) stop-measure-go approach wherein the pipette moves for a predefined distance before measuring its location then the process is repeated until the pipette reaches its destination, and (ii) predictive approach wherein the pipette is continuously tracked and moved. This automated system can be applied for unsupervised single-cell manipulation of neurons in a network, such as electroporation and local delivery of compounds. |
  | Al-Absi, Abdel-Rahman; Qvist, Per; Okujeni, Samora; Khan, Ahmad Raza; Glerup, Simon; Sanchez, Connie; Nyengaard, Jens R Molecular Neurobiology, 2020. @article{Al-Absi2020, title = {Layers II/III of Prefrontal Cortex in Df(h22q11)/+ Mouse Model of the 22q11.2 Deletion Display Loss of Parvalbumin Interneurons and Modulation of Neuronal Morphology and Excitability}, author = {Abdel-Rahman Al-Absi and Per Qvist and Samora Okujeni and Ahmad Raza Khan and Simon Glerup and Connie Sanchez and Jens R. Nyengaard }, url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12035-020-02067-1}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02067-1}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-08-20}, journal = {Molecular Neurobiology}, abstract = {The 22q11.2 deletion has been identified as a risk factor for multiple neurodevelopmental disorders. Behavioral and cognitive impairments are common among carriers of the 22q11.2 deletion. Parvalbumin expressing (PV+) interneurons provide perisomatic inhibition of excitatory neuronal circuits through GABAA receptors, and a deficit of PV+ inhibitory circuits may underlie a multitude of the behavioral and functional deficits in the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. We investigated putative deficits of PV+ inhibitory circuits and the associated molecular, morphological, and functional alterations in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of the Df(h22q11)/+ mouse model of the 22q11.2 hemizygous deletion. We detected a significant decrease in the number of PV+ interneurons in layers II/III of PFC in Df(h22q11)/+ mice together with a reduction in the mRNA and protein levels of GABAA (α3), a PV+ putative postsynaptic receptor subunit. Pyramidal neurons from the same layers further experienced morphological reorganizations of spines and dendrites. Accordingly, a decrease in the levels of the postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD95) and a higher neuronal activity in response to the GABAA antagonist bicuculline were measured in these layers in PFC of Df(h22q11)/+ mice compared with their wild-type littermates. Our study shows that a hemizygotic deletion of the 22q11.2 locus leads to deficit in the GABAergic control of network activity and involves molecular and morphological changes in both the inhibitory and excitatory synapses of parvalbumin interneurons and pyramidal neurons specifically in layers II/III PFC.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The 22q11.2 deletion has been identified as a risk factor for multiple neurodevelopmental disorders. Behavioral and cognitive impairments are common among carriers of the 22q11.2 deletion. Parvalbumin expressing (PV+) interneurons provide perisomatic inhibition of excitatory neuronal circuits through GABAA receptors, and a deficit of PV+ inhibitory circuits may underlie a multitude of the behavioral and functional deficits in the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. We investigated putative deficits of PV+ inhibitory circuits and the associated molecular, morphological, and functional alterations in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of the Df(h22q11)/+ mouse model of the 22q11.2 hemizygous deletion. We detected a significant decrease in the number of PV+ interneurons in layers II/III of PFC in Df(h22q11)/+ mice together with a reduction in the mRNA and protein levels of GABAA (α3), a PV+ putative postsynaptic receptor subunit. Pyramidal neurons from the same layers further experienced morphological reorganizations of spines and dendrites. Accordingly, a decrease in the levels of the postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD95) and a higher neuronal activity in response to the GABAA antagonist bicuculline were measured in these layers in PFC of Df(h22q11)/+ mice compared with their wild-type littermates. Our study shows that a hemizygotic deletion of the 22q11.2 locus leads to deficit in the GABAergic control of network activity and involves molecular and morphological changes in both the inhibitory and excitatory synapses of parvalbumin interneurons and pyramidal neurons specifically in layers II/III PFC. |
  | Idrees, Saad; Baumann, Matthias P; Franke, Felix; Münch, Thomas A; Hafed, Ziad M Perceptual saccadic suppression starts in the retina Journal Article Nature Communications, 11 (1977), 2020. @article{Idrees2020, title = {Perceptual saccadic suppression starts in the retina}, author = {Saad Idrees and Matthias P. Baumann and Felix Franke and Thomas A. Münch and Ziad M. Hafed}, url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-15890-w}, doi = {10.1038/s41467-020-15890-w}, year = {2020}, date = {2020-04-24}, journal = {Nature Communications}, volume = {11}, number = {1977}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
  | Kubota, Tomoyuki; Nakajima, Kohei; Takahashi, Hirokazu Echo State Property of Neuronal Cell Cultures Book Chapter 11731 , Springer, 2019, ISBN: 978-3-030-30493-5. @inbook{Kubota2019b, title = {Echo State Property of Neuronal Cell Cultures}, author = {Tomoyuki Kubota and Kohei Nakajima and Hirokazu Takahashi }, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-030-30493-5_13}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-30493-5_13}, isbn = {978-3-030-30493-5}, year = {2019}, date = {2019-09-09}, volume = {11731}, publisher = {Springer}, abstract = {Physical reservoir computing (PRC) utilizes the nonlinear dynamics of physical systems, which is called a reservoir, as a computational resource. The prerequisite for physical dynamics to be a successful reservoir is to have the echo state property (ESP), asymptotic properties of transient trajectory to driving signals, with some memory held in the system. In this study, the prerequisites in dissociate cultures of cortical neuronal cells are estimated. With a state-of-the-art measuring system of high-dense CMOS array, our experiments demonstrated that each neuron exhibited reproducible spike trains in response to identical driving stimulus. Additionally, the memory function was estimated, which found that input information in the dynamics of neuronal activities in the culture up to at least 20 ms was retrieved. These results supported the notion that the cultures had ESP and could thereby serve as PRC.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inbook} } Physical reservoir computing (PRC) utilizes the nonlinear dynamics of physical systems, which is called a reservoir, as a computational resource. The prerequisite for physical dynamics to be a successful reservoir is to have the echo state property (ESP), asymptotic properties of transient trajectory to driving signals, with some memory held in the system. In this study, the prerequisites in dissociate cultures of cortical neuronal cells are estimated. With a state-of-the-art measuring system of high-dense CMOS array, our experiments demonstrated that each neuron exhibited reproducible spike trains in response to identical driving stimulus. Additionally, the memory function was estimated, which found that input information in the dynamics of neuronal activities in the culture up to at least 20 ms was retrieved. These results supported the notion that the cultures had ESP and could thereby serve as PRC. |
  | Obien, Marie Engelene J; Zorzi, Giulio; Fiscella, Michele; Leary, Noelle; Hierlemann, Andreas Comparison of axonal-conduction velocity in developing primary cells and human iPSC-derived neurons Conference 11th International Meeting on Substrate Integrated Microelectrode Arrays (MEA Meeting) Reutlingen, Germany, 2018. @conference{Obien2018, title = {Comparison of axonal-conduction velocity in developing primary cells and human iPSC-derived neurons}, author = {Marie Engelene J. Obien and Giulio Zorzi and Michele Fiscella and Noelle Leary and Andreas Hierlemann}, url = {https://www.frontiersin.org/10.3389/conf.fncel.2018.38.00095/event_abstract}, doi = {10.3389/conf.fncel.2018.38.00095}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-07-04}, address = {Reutlingen, Germany}, organization = {11th International Meeting on Substrate Integrated Microelectrode Arrays (MEA Meeting)}, abstract = {Neurons communicate through action potentials propagating along axons. In developing cell cultures, axonal arbor outgrowth indicates the formation of synaptic connections between neurons, which form networks. As axons regulate the transfer of information, we hypothesize that axonal conduction characteristics, e.g., axonal action potential amplitude and propagation velocity, may be indicative of the maturation state of cells and the strength of interneuronal connections.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } Neurons communicate through action potentials propagating along axons. In developing cell cultures, axonal arbor outgrowth indicates the formation of synaptic connections between neurons, which form networks. As axons regulate the transfer of information, we hypothesize that axonal conduction characteristics, e.g., axonal action potential amplitude and propagation velocity, may be indicative of the maturation state of cells and the strength of interneuronal connections. |
  | Zorzi, Giulio; Obien, Marie Engelene J; Fiscella, Michele; Leary, Noelle; Hierlemann, Andreas Automatic extraction of axonal arbor morphology applied to h-iPSC-derived neurons Conference 11th International Meeting on Substrate Integrated Microelectrode Arrays (MEA Meeting) Reutlingen, Germany, 2018. @conference{Zorzi2018, title = {Automatic extraction of axonal arbor morphology applied to h-iPSC-derived neurons}, author = {Giulio Zorzi and Marie Engelene J. Obien and Michele Fiscella and Noelle Leary and Andreas Hierlemann}, url = {https://www.frontiersin.org/10.3389/conf.fncel.2018.38.00049/event_abstract}, doi = {10.3389/conf.fncel.2018.38.00049}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-07-04}, address = {Reutlingen, Germany}, organization = {11th International Meeting on Substrate Integrated Microelectrode Arrays (MEA Meeting)}, abstract = {Neurons derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (h-iPSCs) offer tremendous opportunities to investigate the mechanisms involved in brain function and to model neurodegenerative diseases. Analyzing the behavior of h-iPSC-derived neurons that represent the phenotypes of human neurological disorders paves the way for the development of physiologically-relevant models and assays for drug discovery. In this framework, we utilize a CMOS-based high-density microelectrode array (HD-MEA, MaxWell Biosystems) to investigate h-iPSC neurons at sub-cellular resolution. Recording extracellular action potentials (EAPs or spikes) of cultured neurons through microelectrode arrays (MEAs) is a well-established technique for extracting valuable features of neuronal function and network connectivity (Obien et al., Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2015). }, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } Neurons derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (h-iPSCs) offer tremendous opportunities to investigate the mechanisms involved in brain function and to model neurodegenerative diseases. Analyzing the behavior of h-iPSC-derived neurons that represent the phenotypes of human neurological disorders paves the way for the development of physiologically-relevant models and assays for drug discovery. In this framework, we utilize a CMOS-based high-density microelectrode array (HD-MEA, MaxWell Biosystems) to investigate h-iPSC neurons at sub-cellular resolution. Recording extracellular action potentials (EAPs or spikes) of cultured neurons through microelectrode arrays (MEAs) is a well-established technique for extracting valuable features of neuronal function and network connectivity (Obien et al., Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2015). |
  | Shein-Idelson, Mark; Pammer, Lorenz; Hemberger, Mike; Laurent, Gilles Large-scale mapping of cortical synaptic projections with extracellular electrode arrays Journal Article Nature Methods, 14 (9), pp. 882–889, 2017, ISSN: 1548-7091. @article{Shein-Idelson2017, title = {Large-scale mapping of cortical synaptic projections with extracellular electrode arrays}, author = {Mark Shein-Idelson and Lorenz Pammer and Mike Hemberger and Gilles Laurent}, url = {http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/nmeth.4393}, doi = {10.1038/nmeth.4393}, issn = {1548-7091}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-08-14}, journal = {Nature Methods}, volume = {14}, number = {9}, pages = {882--889}, abstract = {Understanding circuit computation in the nervous system requires sampling activity over large neural populations and maximizing the number of features that can be extracted. By combining planar arrays of extracellular electrodes with the three-layered cortex of turtles, we show that synaptic signals induced along individual axons as well as action potentials can be easily captured. Two types of information can be extracted from these signals, the neuronal subtype (inhibitory or excitatory)—whose identification is more reliable than with traditional measures such as action potential width—and a (partial) spatial map of functional axonal projections from individual neurons. Because our approach is algorithmic, it can be carried out in parallel on hundreds of simultaneously recorded neurons. Combining our approach with soma triangulation, we reveal an axonal projection bias among a population of pyramidal neurons in turtle cortex and confirm this bias through anatomical reconstructions.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Understanding circuit computation in the nervous system requires sampling activity over large neural populations and maximizing the number of features that can be extracted. By combining planar arrays of extracellular electrodes with the three-layered cortex of turtles, we show that synaptic signals induced along individual axons as well as action potentials can be easily captured. Two types of information can be extracted from these signals, the neuronal subtype (inhibitory or excitatory)—whose identification is more reliable than with traditional measures such as action potential width—and a (partial) spatial map of functional axonal projections from individual neurons. Because our approach is algorithmic, it can be carried out in parallel on hundreds of simultaneously recorded neurons. Combining our approach with soma triangulation, we reveal an axonal projection bias among a population of pyramidal neurons in turtle cortex and confirm this bias through anatomical reconstructions. |
  | Hillier, Daniel; Fiscella, Michele; Drinnenberg, Antonia; Trenholm, Stuart; Rompani, Santiago B; Raics, Zoltan; Katona, Gergely; Jüttner, Josephine; Hierlemann, Andreas; Rozsa, Balazs; Roska, Botond Causal evidence for retina-dependent and -independent visual motion computations in mouse cortex Journal Article Nature Neuroscience, 20 (7), pp. 960–968, 2017, ISSN: 1097-6256. @article{Hillier2017, title = {Causal evidence for retina-dependent and -independent visual motion computations in mouse cortex}, author = {Daniel Hillier and Michele Fiscella and Antonia Drinnenberg and Stuart Trenholm and Santiago B Rompani and Zoltan Raics and Gergely Katona and Josephine Jüttner and Andreas Hierlemann and Balazs Rozsa and Botond Roska}, url = {http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/nn.4566}, doi = {10.1038/nn.4566}, issn = {1097-6256}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-05-22}, journal = {Nature Neuroscience}, volume = {20}, number = {7}, pages = {960--968}, abstract = {How neuronal computations in the sensory periphery contribute to computations in the cortex is not well understood. We examined this question in the context of visual-motion processing in the retina and primary visual cortex (V1) of mice. We disrupted retinal direction selectivity, either exclusively along the horizontal axis using FRMD7 mutants or along all directions by ablating starburst amacrine cells, and monitored neuronal activity in layer 2/3 of V1 during stimulation with visual motion. In control mice, we found an over-representation of cortical cells preferring posterior visual motion, the dominant motion direction an animal experiences when it moves forward. In mice with disrupted retinal direction selectivity, the over-representation of posterior-motion-preferring cortical cells disappeared, and their responses at higher stimulus speeds were reduced. This work reveals the existence of two functionally distinct, sensory-periphery-dependent and -independent computations of visual motion in the cortex.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } How neuronal computations in the sensory periphery contribute to computations in the cortex is not well understood. We examined this question in the context of visual-motion processing in the retina and primary visual cortex (V1) of mice. We disrupted retinal direction selectivity, either exclusively along the horizontal axis using FRMD7 mutants or along all directions by ablating starburst amacrine cells, and monitored neuronal activity in layer 2/3 of V1 during stimulation with visual motion. In control mice, we found an over-representation of cortical cells preferring posterior visual motion, the dominant motion direction an animal experiences when it moves forward. In mice with disrupted retinal direction selectivity, the over-representation of posterior-motion-preferring cortical cells disappeared, and their responses at higher stimulus speeds were reduced. This work reveals the existence of two functionally distinct, sensory-periphery-dependent and -independent computations of visual motion in the cortex. |
  | Lewandowska, Marta K; Radivojevic, Milos; Jäckel, David; Müller, Jan; Hierlemann, Andreas Cortical axons, isolated in channels, display activity-dependent signal modulation as a result of targeted stimulation Journal Article Frontiers in Neuroscience, 10 , pp. 83, 2016, ISSN: 1662453X. @article{Lewandowska2016, title = {Cortical axons, isolated in channels, display activity-dependent signal modulation as a result of targeted stimulation}, author = {Marta K Lewandowska and Milos Radivojevic and David Jäckel and Jan Müller and Andreas Hierlemann}, url = {https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2016.00083/full}, doi = {10.3389/fnins.2016.00083}, issn = {1662453X}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-03-07}, journal = {Frontiers in Neuroscience}, volume = {10}, pages = {83}, abstract = {Mammalian cortical axons are extremely thin processes that are difficult to study as a result of their small diameter: they are too narrow to patch while intact, and super-resolution microscopy is needed to resolve single axons. We present a method for studying axonal physiology by pairing a high-density microelectrode array with a microfluidic axonal isolation device, and use it to study activity-dependent modulation of axonal signal propagation evoked by stimulation near the soma. Up to three axonal branches from a single neuron, isolated in different channels, were recorded from simultaneously using 10-20 electrodes per channel. The axonal channels amplified spikes such that propagations of individual signals along tens of electrodes could easily be discerned with high signal to noise. Stimulation from 10 up to 160 Hz demonstrated similar qualitative results from all of the cells studied: extracellular action potential characteristics changed drastically in response to stimulation. Spike height decreased, spike width increased, and latency increased, as a result of reduced propagation velocity, as the number of stimulations and the stimulation frequencies increased. Quantitatively, the strength of these changes manifested itself differently in cells at different frequencies of stimulation. Some cells' signal fidelity fell to 80% already at 10 Hz, while others maintained 80% signal fidelity at 80 Hz. Differences in modulation by axonal branches of the same cell were also seen for different stimulation frequencies, starting at 10 Hz. Potassium ion concentration changes altered the behavior of the cells causing propagation failures at lower concentrations and improving signal fidelity at higher concentrations.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Mammalian cortical axons are extremely thin processes that are difficult to study as a result of their small diameter: they are too narrow to patch while intact, and super-resolution microscopy is needed to resolve single axons. We present a method for studying axonal physiology by pairing a high-density microelectrode array with a microfluidic axonal isolation device, and use it to study activity-dependent modulation of axonal signal propagation evoked by stimulation near the soma. Up to three axonal branches from a single neuron, isolated in different channels, were recorded from simultaneously using 10-20 electrodes per channel. The axonal channels amplified spikes such that propagations of individual signals along tens of electrodes could easily be discerned with high signal to noise. Stimulation from 10 up to 160 Hz demonstrated similar qualitative results from all of the cells studied: extracellular action potential characteristics changed drastically in response to stimulation. Spike height decreased, spike width increased, and latency increased, as a result of reduced propagation velocity, as the number of stimulations and the stimulation frequencies increased. Quantitatively, the strength of these changes manifested itself differently in cells at different frequencies of stimulation. Some cells' signal fidelity fell to 80% already at 10 Hz, while others maintained 80% signal fidelity at 80 Hz. Differences in modulation by axonal branches of the same cell were also seen for different stimulation frequencies, starting at 10 Hz. Potassium ion concentration changes altered the behavior of the cells causing propagation failures at lower concentrations and improving signal fidelity at higher concentrations. |
  | Müller, Jan; Ballini, Marco; Livi, Paolo; Chen, Yihui; Radivojevic, Milos; Shadmani, Amir; Viswam, Vijay; Jones, Ian L; Fiscella, Michele; Diggelmann, Roland; Stettler, Alexander; Frey, Urs; Bakkum, Douglas J; Hierlemann, Andreas High-resolution CMOS MEA platform to study neurons at subcellular, cellular, and network levels Journal Article Lab Chip, 15 (13), pp. 2767-2780, 2015, ISSN: 1473-0197. @article{Muller2015, title = {High-resolution CMOS MEA platform to study neurons at subcellular, cellular, and network levels}, author = {Jan Müller and Marco Ballini and Paolo Livi and Yihui Chen and Milos Radivojevic and Amir Shadmani and Vijay Viswam and Ian L Jones and Michele Fiscella and Roland Diggelmann and Alexander Stettler and Urs Frey and Douglas J Bakkum and Andreas Hierlemann}, url = {http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2015/LC/C5LC00133A#!divAbstract}, doi = {10.1039/C5LC00133A}, issn = {1473-0197}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-07-07}, journal = {Lab Chip}, volume = {15}, number = {13}, pages = {2767-2780}, publisher = {Royal Society of Chemistry}, abstract = {Studies on information processing and learning properties of neuronal networks would benefit from simultaneous and parallel access to the activity of a large fraction of all neurons in such networks. Here, we present a CMOS-based device, capable of simultaneously recording the electrical activity of over a thousand cells in in vitro neuronal networks. The device provides sufficiently high spatiotemporal resolution to enable, at the same time, access to neuronal preparations on subcellular, cellular, and network level. The key feature is a rapidly reconfigurable array of 26 400 microelectrodes arranged at low pitch (17.5 um) within a large overall sensing area (3.85 × 2.10 mm2). An arbitrary subset of the electrodes can be simultaneously connected to 1024 low-noise readout channels as well as 32 stimulation units. Each electrode or electrode subset can be used to electrically stimulate or record the signals of virtually any neuron on the array. We demonstrate the applicability and potential of this device for various different experimental paradigms: large-scale recordings from whole networks of neurons as well as investigations of axonal properties of individual neurons.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Studies on information processing and learning properties of neuronal networks would benefit from simultaneous and parallel access to the activity of a large fraction of all neurons in such networks. Here, we present a CMOS-based device, capable of simultaneously recording the electrical activity of over a thousand cells in in vitro neuronal networks. The device provides sufficiently high spatiotemporal resolution to enable, at the same time, access to neuronal preparations on subcellular, cellular, and network level. The key feature is a rapidly reconfigurable array of 26 400 microelectrodes arranged at low pitch (17.5 um) within a large overall sensing area (3.85 × 2.10 mm2). An arbitrary subset of the electrodes can be simultaneously connected to 1024 low-noise readout channels as well as 32 stimulation units. Each electrode or electrode subset can be used to electrically stimulate or record the signals of virtually any neuron on the array. We demonstrate the applicability and potential of this device for various different experimental paradigms: large-scale recordings from whole networks of neurons as well as investigations of axonal properties of individual neurons. |
  | Krol, Jacek; Krol, Ilona; Alvarez, Claudia Patricia Patino; Fiscella, Michele; Hierlemann, Andreas; Roska, Botond; Filipowicz, Witold A network comprising short and long noncoding RNAs and RNA helicase controls mouse retina architecture. Journal Article Nature Communications, 6 , pp. 7305, 2015, ISSN: 2041-1723. @article{Krol2015, title = {A network comprising short and long noncoding RNAs and RNA helicase controls mouse retina architecture.}, author = {Jacek Krol and Ilona Krol and Claudia Patricia Patino Alvarez and Michele Fiscella and Andreas Hierlemann and Botond Roska and Witold Filipowicz}, url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms8305}, doi = {10.1038/ncomms8305}, issn = {2041-1723}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-06-04}, journal = {Nature Communications}, volume = {6}, pages = {7305}, publisher = {Nature Publishing Group}, abstract = {Brain regions, such as the cortex and retina, are composed of layers of uniform thickness. The molecular mechanism that controls this uniformity is not well understood. Here we show that during mouse postnatal development the timed expression of Rncr4, a retina-specific long noncoding RNA, regulates the similarly timed processing of pri-miR-183/96/182, which is repressed at an earlier developmental stage by RNA helicase Ddx3x. Shifting the timing of mature miR-183/96/182 accumulation or interfering with Ddx3x expression leads to the disorganization of retinal architecture, with the photoreceptor layer being most affected. We identify Crb1, a component of the adhesion belt between glial and photoreceptor cells, as a link between Rncr4-regulated miRNA metabolism and uniform retina layering. Our results suggest that the precise timing of glia-neuron interaction controlled by noncoding RNAs and Ddx3x is important for the even distribution of cells across layers.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Brain regions, such as the cortex and retina, are composed of layers of uniform thickness. The molecular mechanism that controls this uniformity is not well understood. Here we show that during mouse postnatal development the timed expression of Rncr4, a retina-specific long noncoding RNA, regulates the similarly timed processing of pri-miR-183/96/182, which is repressed at an earlier developmental stage by RNA helicase Ddx3x. Shifting the timing of mature miR-183/96/182 accumulation or interfering with Ddx3x expression leads to the disorganization of retinal architecture, with the photoreceptor layer being most affected. We identify Crb1, a component of the adhesion belt between glial and photoreceptor cells, as a link between Rncr4-regulated miRNA metabolism and uniform retina layering. Our results suggest that the precise timing of glia-neuron interaction controlled by noncoding RNAs and Ddx3x is important for the even distribution of cells across layers. |
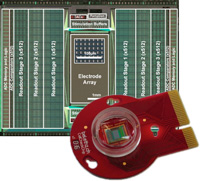  | Ballini, Marco; Müller, Jan; Livi, Paolo; Chen, Yihui; Frey, Urs; Stettler, Alexander; Shadmani, Amir; Viswam, Vijay; Jones, Ian L; Jäckel, David; Radivojevic, Milos; Lewandowska, Marta K; Gong, Wei; Fiscella, Michele; Bakkum, Douglas J; Heer, Flavio; Hierlemann, Andreas A 1024-channel CMOS microelectrode array with 26,400 electrodes for recording and stimulation of electrogenic cells in vitro Journal Article IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 49 (11), pp. 2705-2719, 2014, ISSN: 00189200. @article{Ballini2014, title = {A 1024-channel CMOS microelectrode array with 26,400 electrodes for recording and stimulation of electrogenic cells in vitro}, author = {Marco Ballini and Jan Müller and Paolo Livi and Yihui Chen and Urs Frey and Alexander Stettler and Amir Shadmani and Vijay Viswam and Ian L Jones and David Jäckel and Milos Radivojevic and Marta K Lewandowska and Wei Gong and Michele Fiscella and Douglas J Bakkum and Flavio Heer and Andreas Hierlemann}, url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6923484/}, doi = {10.1109/JSSC.2014.2359219}, issn = {00189200}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-10-14}, journal = {IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits}, volume = {49}, number = {11}, pages = {2705-2719}, abstract = {To advance our understanding of the functioning of neuronal ensembles, systems are needed to enable simultaneous recording from a large number of individual neurons at high spa-tiotemporal resolution and good signal-to-noise ratio. Moreover, stimulation capability is highly desirable for investigating, for example, plasticity and learning processes. Here, we present a microelectrode array (MEA) system on a single CMOS die for in vitro recording and stimulation. The system incorporates 26,400 platinum electrodes, fabricated by in-house post-processing, over a large sensing area (3.85 2.10 mm) with sub-cellular spatial resolution (pitch of 17.5 µm). Owing to an area and power efficient implementation, we were able to integrate 1024 readout channels on chip to record extracellular signals from a user-specified selection of electrodes. These channels feature noise values of 2.4 µV in the action-potential band (300 Hz–10 kHz) and 5.4 µV in the local-field-potential band (1 Hz–300 Hz), and provide programmable gain (up to 78 dB) to accommodate various biological preparations. Amplified and filtered signals are digitized by 10 bit parallel single-slope ADCs at 20 kSamples/s. The system also includes 32 stimulation units, which can elicit neural spikes through either current or voltage pulses. The chip consumes only 75 mW in total, which obviates the need of active cooling even for sensitive cell cultures.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } To advance our understanding of the functioning of neuronal ensembles, systems are needed to enable simultaneous recording from a large number of individual neurons at high spa-tiotemporal resolution and good signal-to-noise ratio. Moreover, stimulation capability is highly desirable for investigating, for example, plasticity and learning processes. Here, we present a microelectrode array (MEA) system on a single CMOS die for in vitro recording and stimulation. The system incorporates 26,400 platinum electrodes, fabricated by in-house post-processing, over a large sensing area (3.85 2.10 mm) with sub-cellular spatial resolution (pitch of 17.5 µm). Owing to an area and power efficient implementation, we were able to integrate 1024 readout channels on chip to record extracellular signals from a user-specified selection of electrodes. These channels feature noise values of 2.4 µV in the action-potential band (300 Hz–10 kHz) and 5.4 µV in the local-field-potential band (1 Hz–300 Hz), and provide programmable gain (up to 78 dB) to accommodate various biological preparations. Amplified and filtered signals are digitized by 10 bit parallel single-slope ADCs at 20 kSamples/s. The system also includes 32 stimulation units, which can elicit neural spikes through either current or voltage pulses. The chip consumes only 75 mW in total, which obviates the need of active cooling even for sensitive cell cultures. |
Discover More
Would you like to learn more about MaxOne? Book a one-to-one call with one of our scientist to discuss how MaxWell Biosystems’ high-content electrophysiology solutions can bring new key insights to your project or request a quote.
Support
We provide training and support on all aspects of the MaxTwo platform. We have the expertise to help you design experiments and/or analysis tools and integrate MaxTwo with your automation system.
Ask a Question English
English